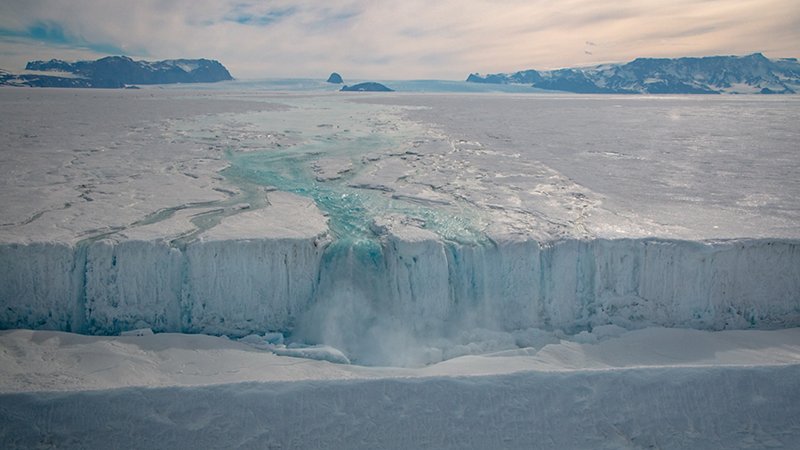
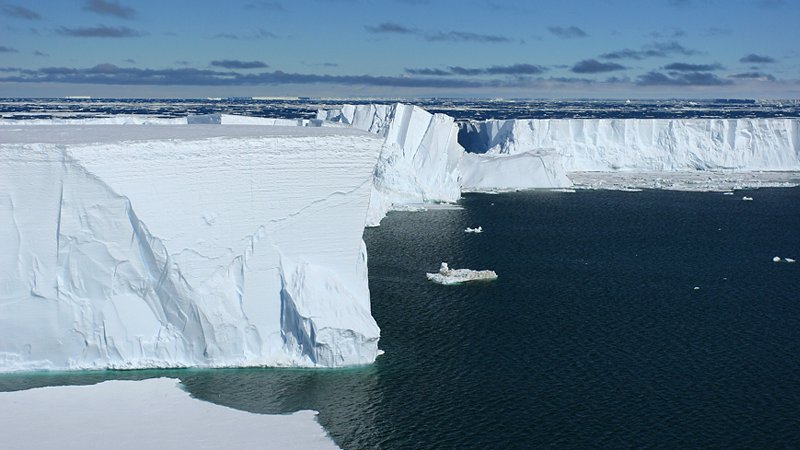
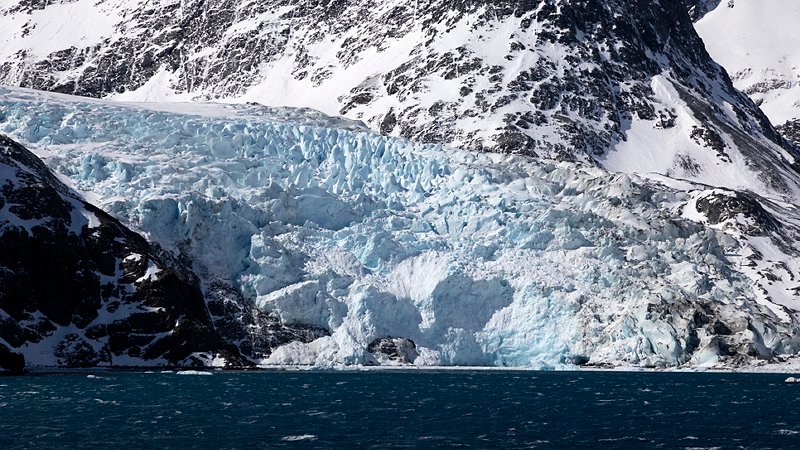
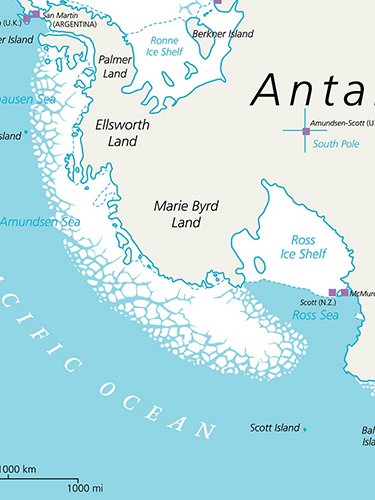
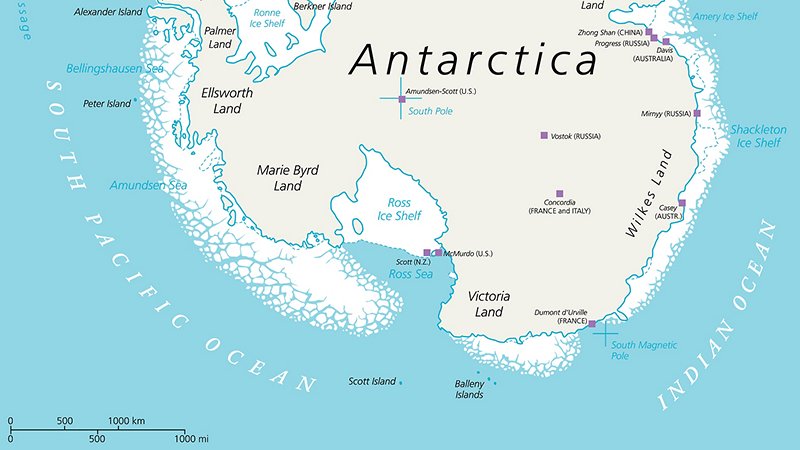
Terranova Bay is a broad inlet in the Ross Sea that has the singular characteristic of always being free from sea ice , due to the presence of the ice tongue of the Drygalski Glacier and the strong winds that blow from land towards the sea. The winds, in fact, often blowing at over 200 km/hr, push the forming sea ice towards the open sea, while the Drygalski tongue inhibits the entrance into the bay of sea ice formed elsewhere and pushed along by the currents. This body of water that remains free from ice, allows a great exchange of heat between the masses of cold air that come from the ice cap and the ocean waters and this has important repercussions on the global ocean circulation. Also, due to the fact that the sea ice that has just formed gets pushed away, Terranova Bay produces 10 to 30% of the sea ice produced in the Ross Sea, even though it accounts for only 1% of its surface: this implies that it is one of the planet’s most important ‘ice factories’, and it is clear that its study is of great importance to understand the behaviour of the planet itself.