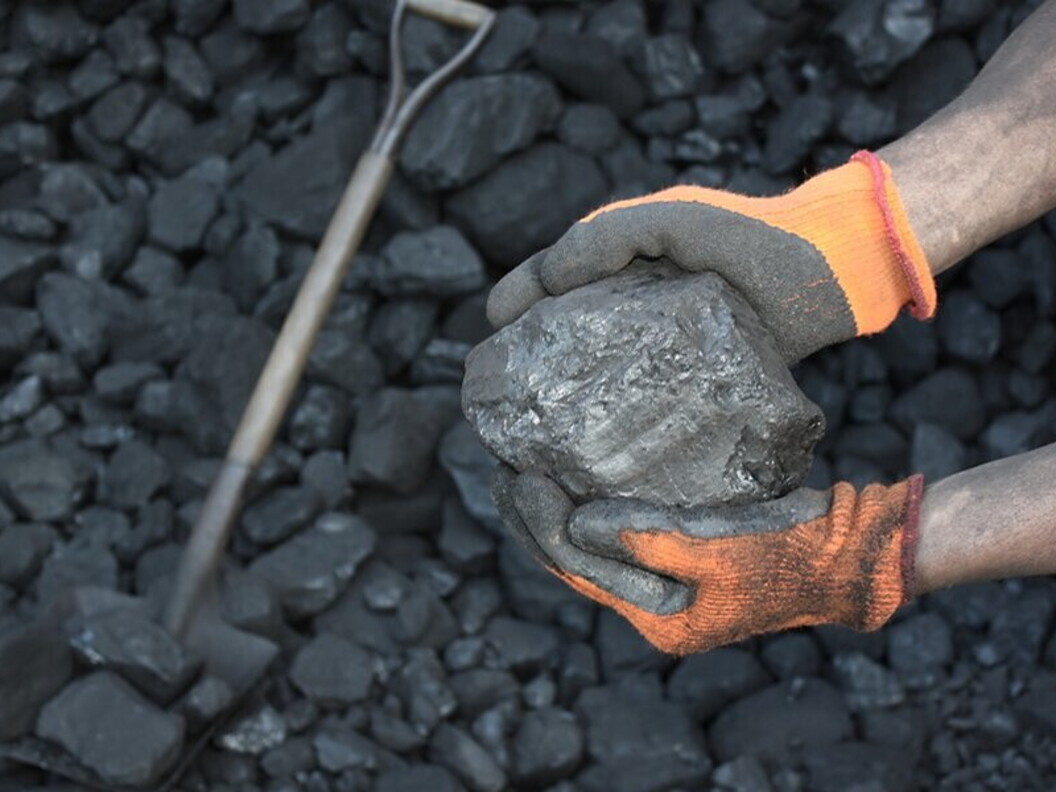
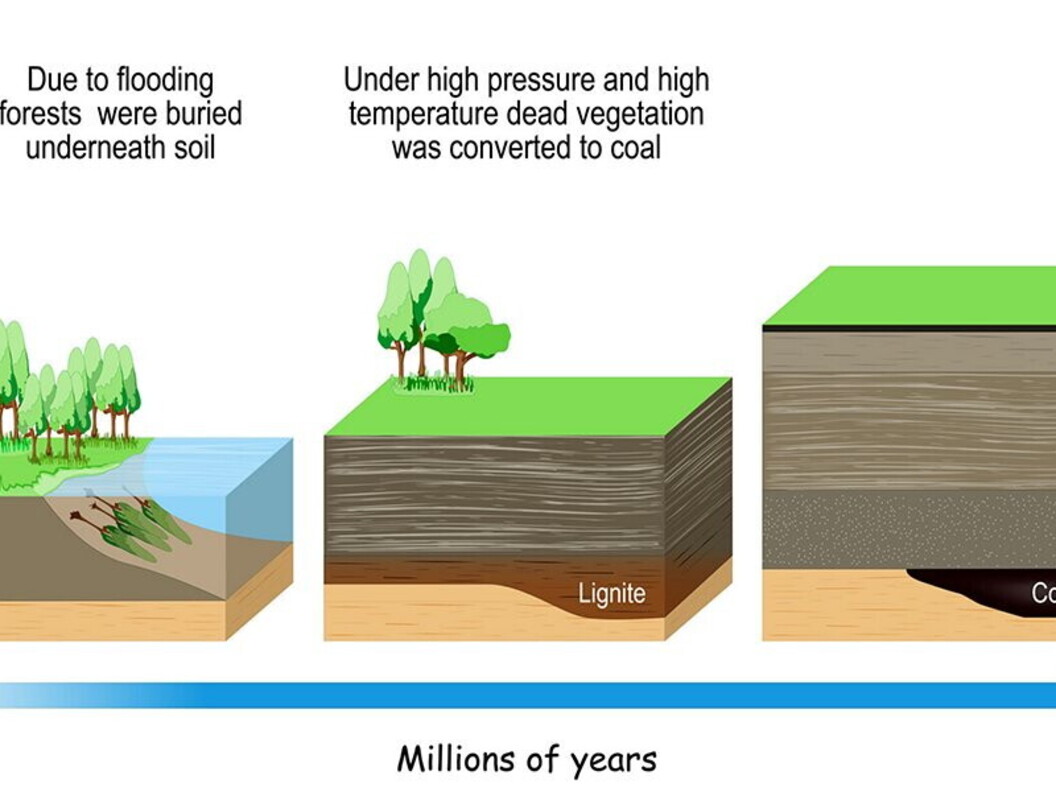
Coal is a fossil fuel just like oil and natural gas. Unlike them, coal is a solid fuel and as such it is the most exploited solid fuel for the production of electric energy in the world. Their different state is explained by the different origin of such three fuels. Whereas oil and natural gas come from the rests of microscopic organisms living in water (plankton, seashells, coral, etc.) deposited at the bottom of ancient seas, coal formed from the rests of plants of the past, the structure and form of which, albeit modified, can still be identified by means of a microscope.
Carbon is the main component of coal after the other basic components of the original living matter (hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen) progressively decayed during chemical and physical processes transforming it. The combustion of coal frees the energy of the sun stored in plants thanks to the photosynthesis millions of years ago: therefore it is an invaluable container of “fossil” solar energy.