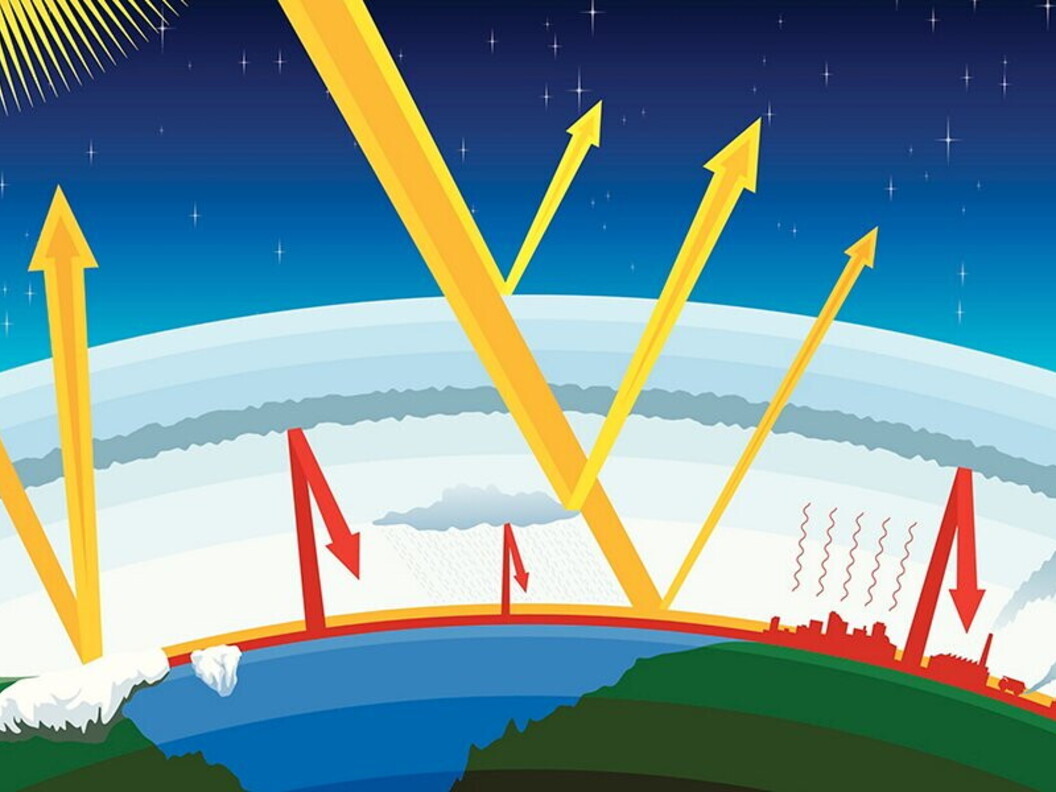
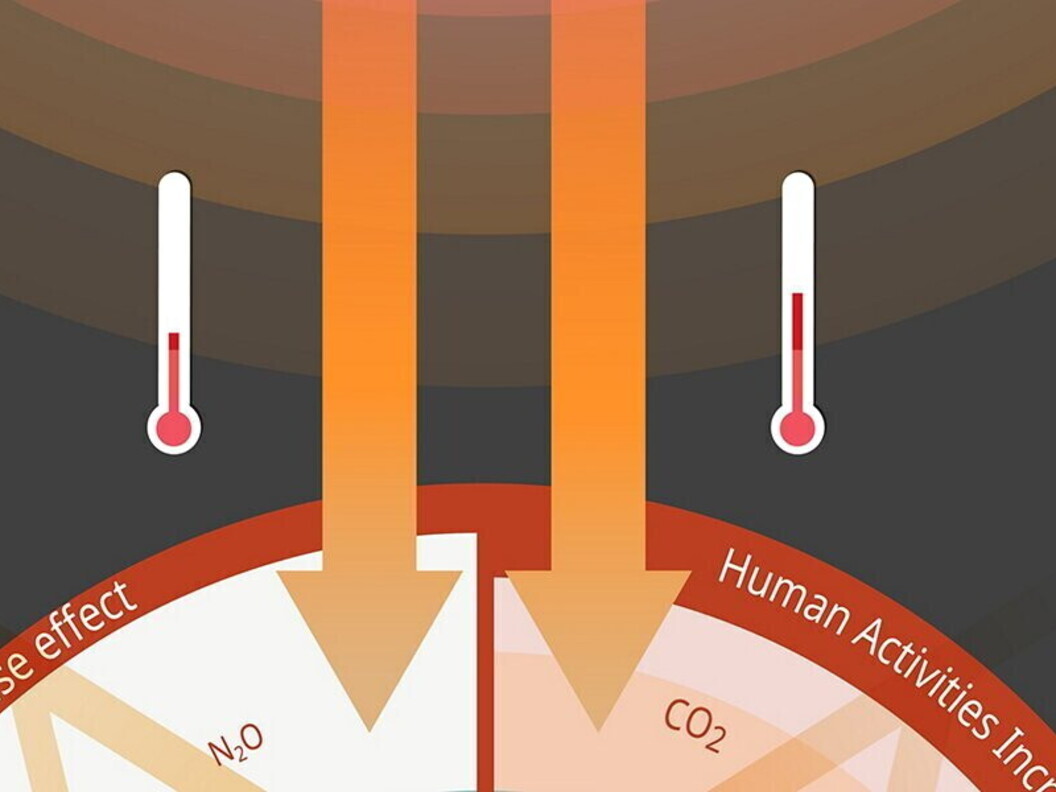
A greenhouse is a closed and controlled environment where plants grow at a constant level of temperature and humidity. It is a method of cultivation that cancels the effects of the seasons because the weather within a greenhouse is always fine. The system works because of the transparent glass or plastic roof and walls that trap the heat of the sun inside the greenhouse. The greenhouse effect does something similar: greenhouse gases trap a little solar energy in the atmosphere and heat the planet.
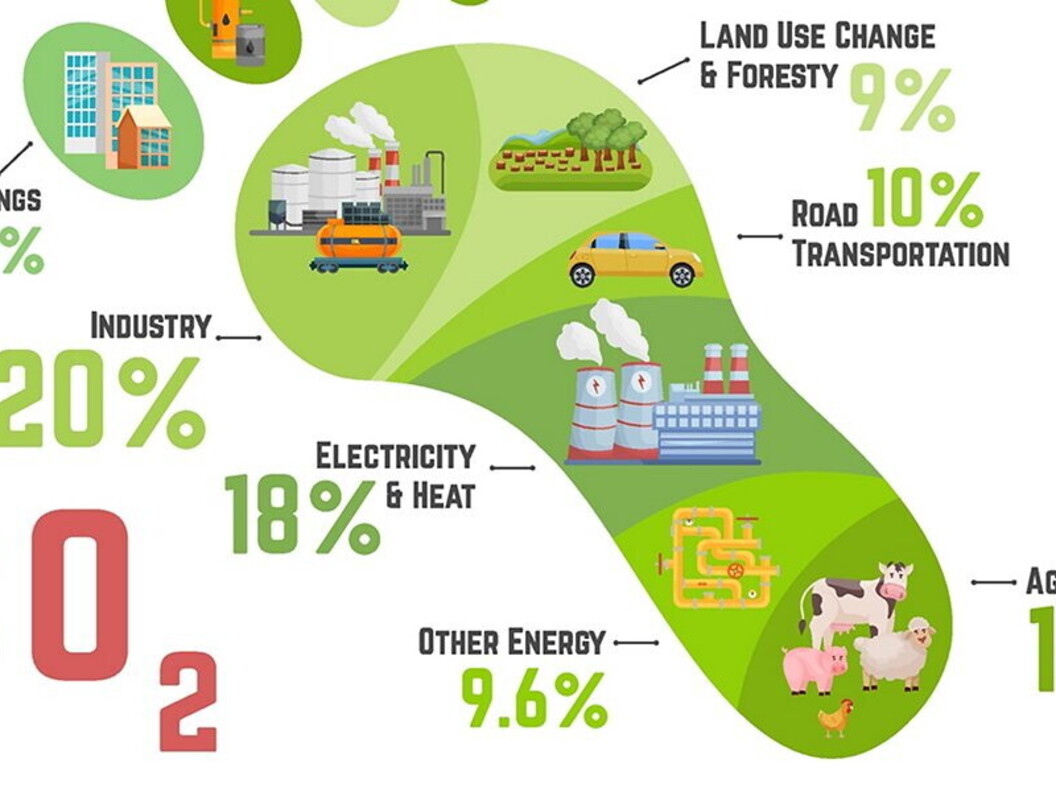
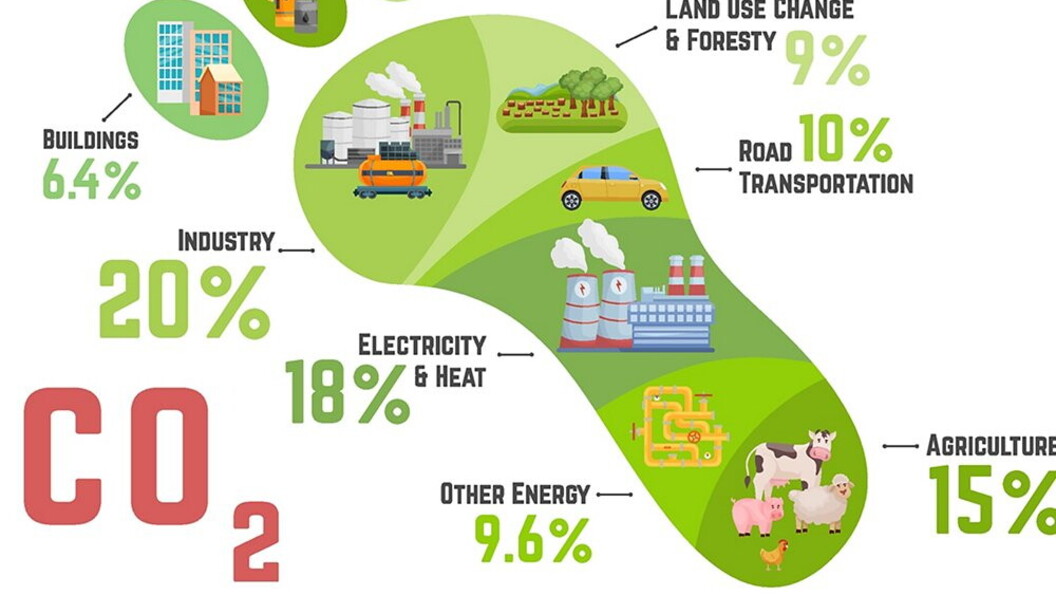
Carbon dioxide is the gas that contributes most to the greenhouse effect (60%), followed by methane (20%), ozone (15%), nitrogen oxides (10%) and chlorofluorocarbons (5%). While carbon dioxide, ozone, methane and nitrogen oxides are for the most part of natural origin, chlorofluorocarbons are artificial; they are gases once used in refrigerators and in spray cannisters and, given that they have caused the famous ozone hole, they were banned in 1990, but they are gases with long life-spans and those that are still in circulation continue to cause damage.