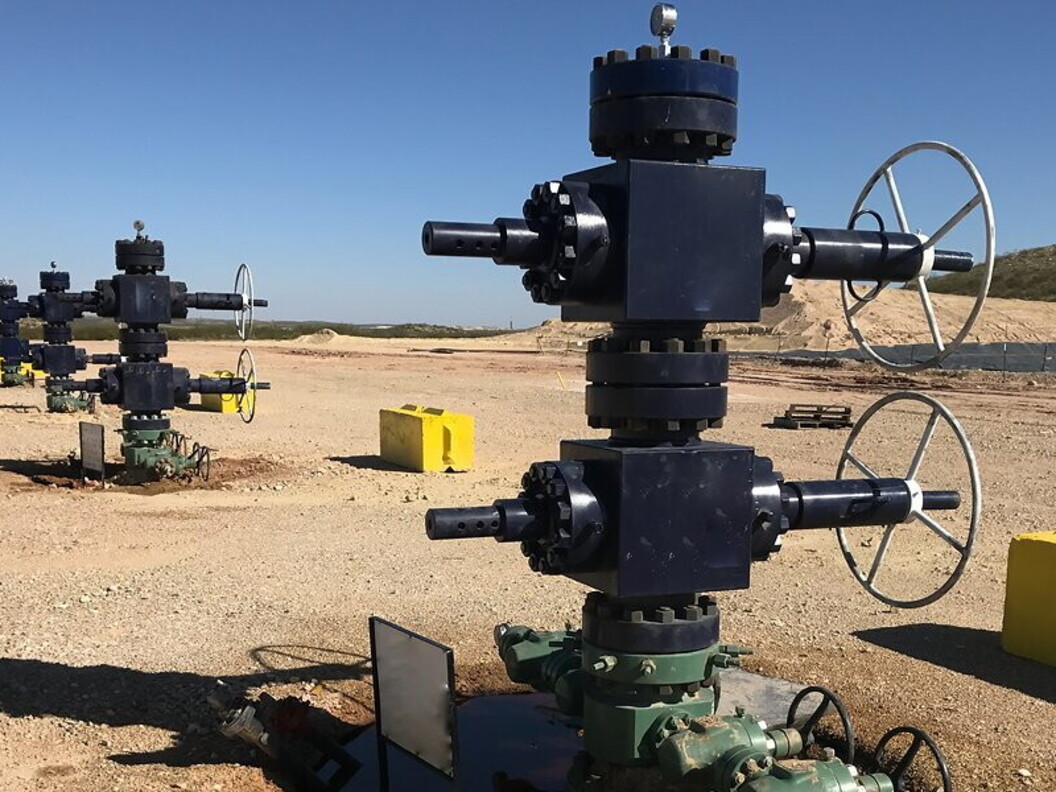
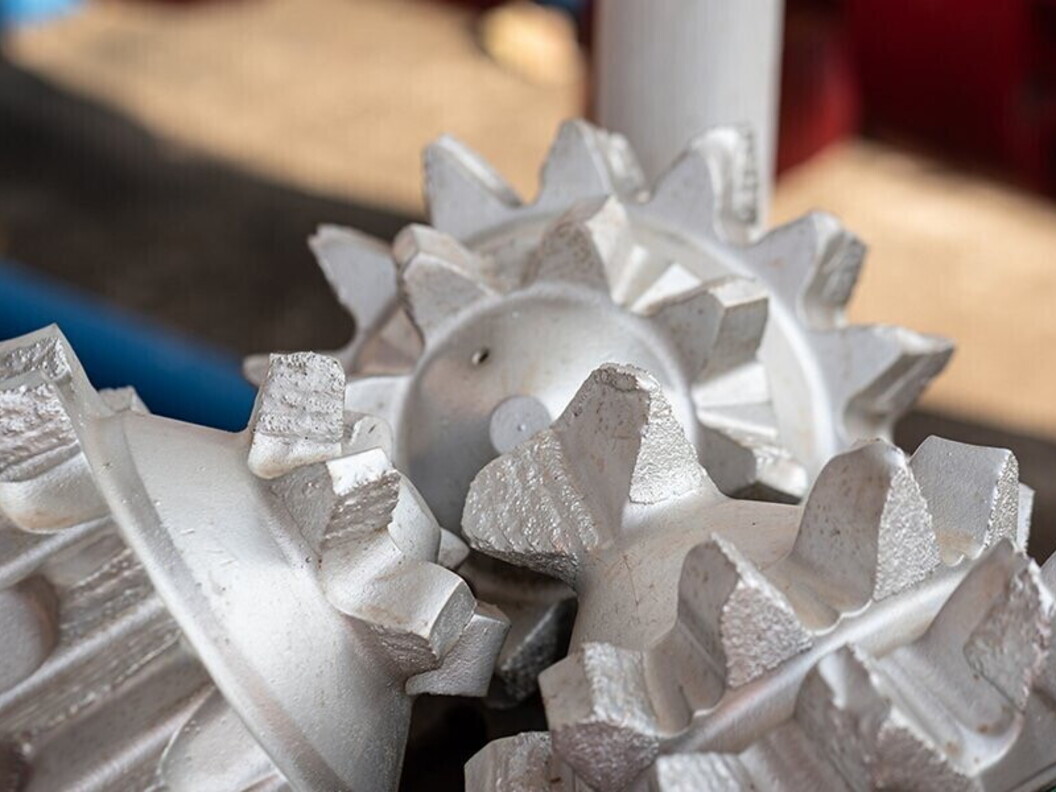
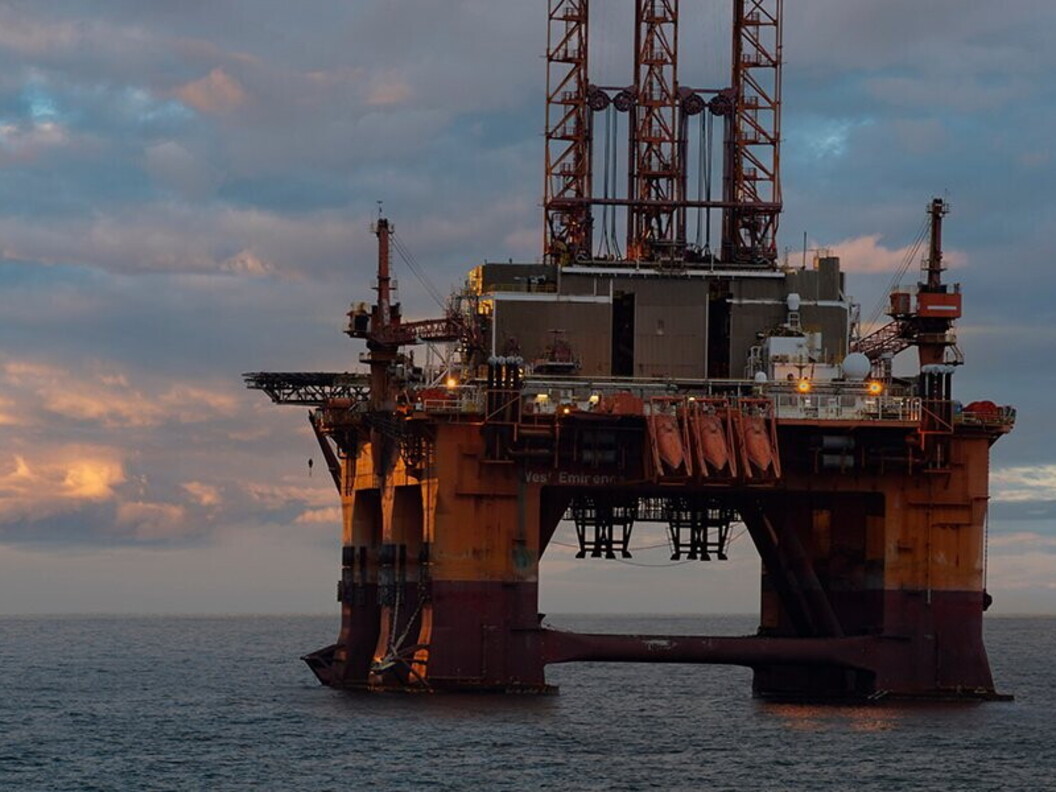
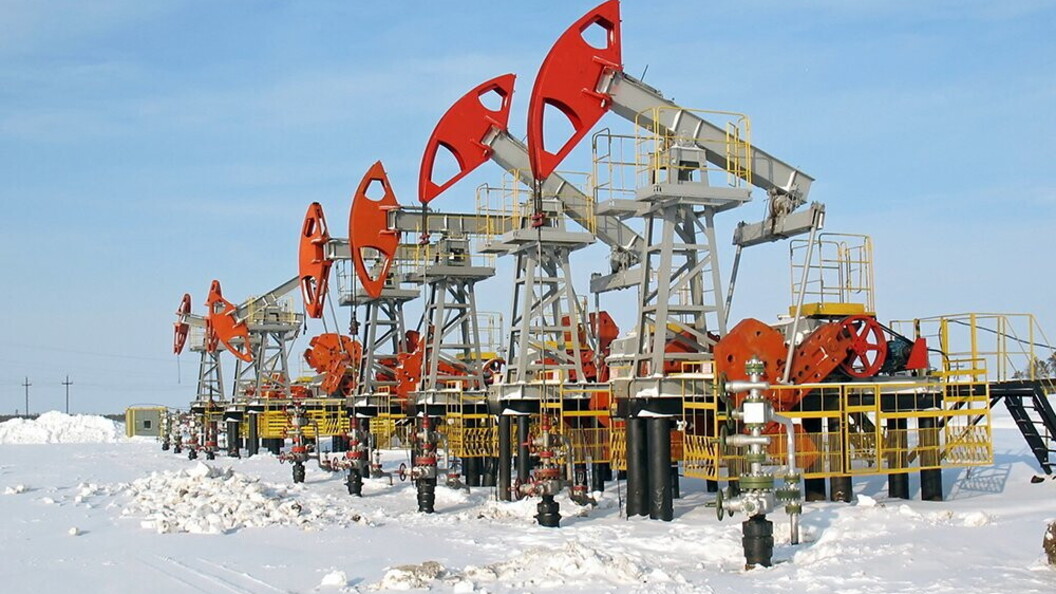
Pumpjack
On extraction, crude oil contains a mixture of hydrocarbons along with water, dissolved natural gas, salts, sulphur and inert substances such as sand and heavy metals. Prior to being introduced into the pipelines, crude oil must undergo a number of processes such as degasification, dehydration, desalting and desulphurisation. After having undergone the different processes, crude oil is generally stored in cylindrical steel tanks, which are fire resistant and equipped with a cooling system and containment basins in case of rupture of the tank, until it is transported to refineries by oil tankers and transmission pipeline.